Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that leaves the atmosphere more quickly than carbon dioxide but traps more heat while it is there – as much as 36 times more over a 100-year timescale, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Methane is responsible for about 30% of the rise in global temperatures since the start of the Industrial Revolution. The UN estimates that a 45% drop in anthropogenic methane emissions would prevent about 0.3°C of warming by 2045. Although methane comes from a variety of sources, minimizing methane emissions from the energy sector is one of the most efficient ways to make a dent in climate change.
Next Available Course: Spring 2024

Methane is responsible for around 30% of the rise in global temperatures since the industrial revolution, and rapid and sustained reductions in methane emissions are key to limit near-term warming and improve air quality.
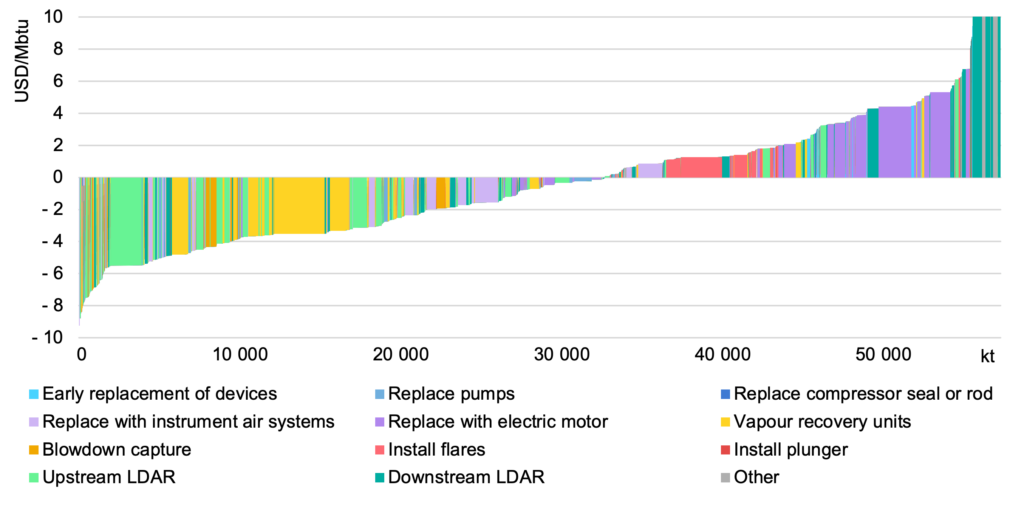
Source: IEA
Two key characteristics determine the impact of different greenhouse gases on the climate: the length of time they remain in the atmosphere and their ability to absorb energy. Methane has a much shorter atmospheric lifetime than carbon dioxide (CO2) – around 12 years compared with centuries – but absorbs much more energy while it exists in the atmosphere. One metric ton of methane is equivalent to about 29 metric tons of carbon dioxide considering its impact over 100 years, and 82 metric tons over a 20-year time horizon.
According to a paper by the IEA, the Climate and Clean Air Coalition and the United Nations Environment Programme, available methane abatement measures can simultaneously: reduce human-caused methane emissions by as much as 45%; improve air quality, thereby saving hundreds of thousands of lives; contribute to food security by preventing crop losses; and create jobs through mitigation efforts. This paper finds that rapid cuts in methane emissions from fossil fuels could avoid up to 0.1°C in global temperature rise by mid-century – greater than the emissions impact of immediately taking all cars and trucks in the world off the road.
The IEA has also found that the oil and gas sector accounts for over 20% of methane emissions from human activity. Tackling methane emissions in this sector represents one of the best near-term opportunities for limiting global warming, because the pathways for reducing them are well known and often cost-effective. Considering natural gas prices seen in recent years, over 40% of emissions from oil and gas operations worldwide could be abated at no net cost, as abatement measures cost less than the market value of the additional gas that would be captured. These elevated gas prices mean that almost all of the options to reduce emissions from oil and gas operations worldwide could be implemented at near-zero net cost.
Better methane management, alongside the reduction of flaring, would also improve energy security. According to the World Bank, over 139 billion cubic meters of gas was flared in 2022. Tackling flaring, venting and fugitive emissions benefits the climate, ensures the safety of workers, improves air quality and increases energy security. While not a substitute for the imperative need to reach carbon dioxide neutrality, methane mitigation is an effective lever to limit future warming and associated damage to social and natural systems.